A curated list of SNMP commands and parameters.
The article aims to highlight differences between RedHat (e.g. AlmaLinux/CentOS) based distributions and Debian (e.g. Ubuntu) based distributions. As a bonus how to setup SNMP on Windows is included.
As a bonus we include a distribution detection script which may be used with automation software.
Table of Contents
Distro detection script
If you’re using LibreNMS or you want your SNMP management application to automatically detect the distribution, use this script:
curl -o /usr/bin/distro https://raw.githubusercontent.com/librenms/librenms-agent/master/snmp/distro; chmod +x /usr/bin/distro
Install on Debian/Ubuntu
apt install snmpd
Install on AlmaLinux
dnf install net-snmp systemctl enable snmpd
Install on CentOS
yum install net-tools chkconfig snmpd on (CentOS 6) systemctl enable snmpd (CentOS 7)
Configuration
One line Bash installer script for Debian/Ubuntu
Only for a fresh system:
sudo apt install snmpd;mv /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf.bak;echo rocommunity secret a.b.c.d >> /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf;service snmpd restart;
- Change
secretanda.b.c.din the script before running it - Add UDP port 161 to your firewall
- Restart your firewall after adding port 161
The script creates this file /etc/snmpd/snmpd.conf:
rocommunity secret a.b.c.d
If you change /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf with another secret or IP address and restart snmpd again.
Here is a more extensive template:
rocommunity your_secret_public_community syslocation Rack, Room, Building, City, Country syscontact Your Name <[email protected]> sysDescr Hardware, Serial, Operating System, Platform #Distro Detection extend distro /usr/bin/distro
If you don’t have serial numbers for sysDescr, you could do something like:
sysDescr Guest, Host, Control Panel, Major Applications
E.g.:
sysDescr VM on SuperDaddy, Dedicated Machine at XYZ, Virtualmin, Email + Web
Ubuntu
Configuration
The quick single line way works:
rocommunity your_secret_public_community ip_address_of_snmp_server
Change a.b.c.d in the script or in /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf with the right IP address and then restart snmpd again if needed.
Also add UDP 161 to your firewall.
Here is a more extensive Ubuntu template:
rocommunity your_secret_public_community syslocation Rack, Room, Building, City, Country syscontact Your Name <[email protected]> com2sec readonly your_secret_public_community agentaddress udp:161 sysservices 76 master yes
Windows Server
Windows server setup is UI driven. There are three steps:
- Install the Windows server feature using the server management tool
- Add Roles and Features Wizard
- Next, next, next, click on Features
- SNMP Service which will auto suggest it’s SNMP Tools dependency. You only need those two services.
- On some systems it’s rather called SNMP Service, already select (but 0 installed?), and it’s child is SNMP WMI Provider.
- Next, next, next, click on Features
- Add Roles and Features Wizard
- In services.exe, right click the newly installed SNMP Service and change on the last tab, both the authentication (e.g. public) and IP address allowed. If you’ve just installed the service you might have to wait around a minute or two for actual right click menus that you need to appear.
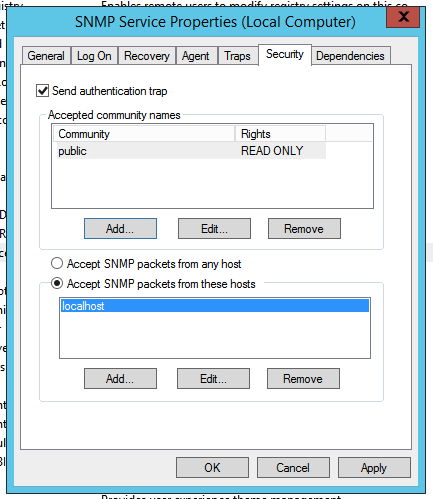
Change localhost to the IP address of your management server.
Enable UDP port 161 in using the firewall tool for the public zone. This might be optional on some systems.
Other Linux
A curated set of configuration commands and options that should work with any distribution
Allow Firewalld
If you’re using Firewalld, use these two commands to quickly allow SNMP through:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=snmp; firewall-cmd --reload
Turn off Repetitive Logging
Is your syslog overrun with SNMP connect requests? Try this:
dontLogTCPWrappersConnects yes
Execute your own OID Script
Postfix
This parameter works in conjunction with another script to calculate Postfix queue size.
exec postqueue /etc/postfix/snmp_monitor_postqueue.sh
When you have this as the first “application” for SNMPD, the OID will be:
| .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.8.1.101.1 |
Monitoring Asterisk
When monitoring Asterisk, you might end with these four entries:
exec AsteriskExtensionInUse /usr/bin/sudo /etc/snmp/asterisk_extension_in_use.sh exec AsteriskExtensionNotInUse /usr/bin/sudo /etc/snmp/asterisk_extension_not_in_use.sh exec AsteriskExtensionUnavailable /usr/bin/sudo /etc/snmp/asterisk_extension_unavailable.sh exec AsteriskExtensionRinging /usr/bin/sudo /etc/snmp/asterisk_extension_ringing.sh
Testing with SNMPWalk
A beautiful elegant savvy way of testing your SNMP 😉
For AlmaLinux or CentOS, you need this:
dnf install net-snmp-utils or yum install net-snmp-utils
Then do this:
snmpwalk -c your_secret -v1 host.example.com
If you’re testing from afar, maybe also try testing on localhost first like so:
snmpwalk -c your_secret -v1 localhost
If it ain’t working, you’ll get this:
# snmpwalk -c secret -v1 localhost
Timeout: No Response from localhost
If you’re unsure if UDP is open, first test from to 127.0.0.1. Intentionally don’t test to localhost, because it might revert to IPv6:
nping -udp -p 161 server.example.com
or with NMAP:
sudo nmap -sU -p 161 server.example.com
or if nc exists:
nc -zvu 127.0.0.1 161 Ncat: Version 7.92 ( https://nmap.org/ncat ) Ncat: Connected to 127.0.0.1:161. Ncat: UDP packet sent successfully Ncat: 1 bytes sent, 0 bytes received in 2.07 seconds.
`nc` might also return no route to host if there is a firewall(d) issue.
Other Interesting Parameters
cat /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf # run as # agentuser root # realStorageUnits 0